CSRD timeline: what you need to report and when

Published: June 2023
Around 50 000 companies operating in the European Union are expected to be impacted by the EU’s new Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). The CSRD, in a nutshell, can be described as the new and improved version of the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). CSRD aims to increase the transparency into companies' impact on the planet and people by getting them to step up their sustainability disclosure game with stricter and more transparent reporting standards.
The CSRD got the green light at the beginning of 2023, and the clock is ticking for the first batch of companies required to comply with the directive's requirement for their 2024 fiscal year’s reporting. But don't worry; we've got you covered!
This blog will give you all the details you need, including the key dates, what companies have to report when, and how you can comply with the CSRD.
What are the CSRD requirements?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) has established some standard rules for companies to follow when creating their annual sustainability reports. Basically, you’ll have to include:
- Double materiality: Companies must analyze their sustainability impact through two different types of materiality, which are how their business impacts people and the planet, and how sustainability and climate change impact their business.
- ESRS: Companies must follow the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) when conducting their sustainability reporting. These standards cover environmental, social, and governance topics.
- Third-party assurance: The CSRD requires companies to provide limited assurance for their sustainability information. This means that an impartial, reliable, and knowledgeable third party must review the data to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
- The information must be a part of the management report and published in a digital format (XHTML).
What are the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS)?
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) is a set of standards that companies must adhere to during their sustainability reporting process to comply with the CSRD.
The ESRS covers four key topics that must be included in sustainability reports, which are:
- General reporting requirements: Provides the framework for how to report the information required.
- Environmental impact: Cover the topics on climate change, pollution, water, marine resources, biodiversity, and ecosystems.
- Social responsibility: Cover the topics of the company’s own workforce, workers in the value chain, affected communities, and customers & end-users.
- Governance: Cover business conduct.
The standards are still in draft but are expected to be approved in June 2023. Plus, the EFRAG (which are the ones behind the standards) have also announced that they’ll also create ten sector-specific standards that will require companies in high-impact sectors (such as energy production, road transport, motor vehicle production, food/beverages and textiles) and or energy-intensive sectors to disclose more information.
What about the CSRD timeline?
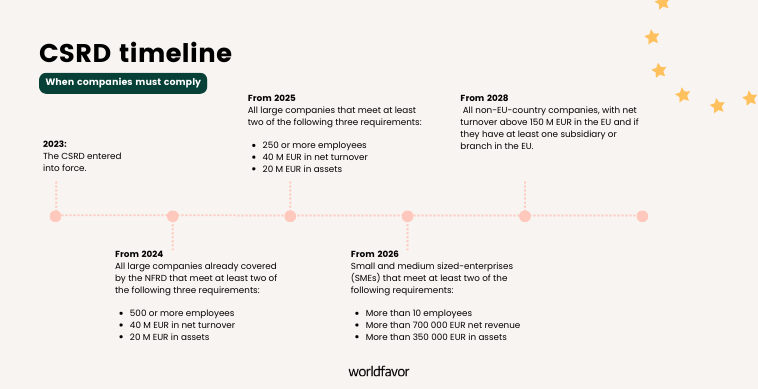
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) has been in effect since January 2023, and its implementation is being phased over the next few years, depending on the size of the companies. To help you stay on top of things, here's a breakdown of the key dates and details for each phase:
The first phase: 1st January 2024
Companies affected:
Large companies with over 500 employees that are already subject to the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFDR).
The “first-phase” companies must start reporting according to the CSRD requirements for the 2024 fiscal year, with the report to be published in 2025.
The second phase: 1st January 2025
Companies affected:
From this phase on, the first set of companies that weren’t previously subject to the NFDR will need to comply with the CSRD requirements. This applies to large companies that meet at least two out of three specified requirements:
- More than 250 employees and/or
- 40 million EUR in turnover and/ or
- 20 million EUR in total assets
Companies in the second phase will have to start reporting according to the CSRD requirements in 2025, with the reports to be published in 2026.
The third phase: 1st January 2026
Companies affected:
From the 1st of January 2026, the CSRD will also be applied to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) listed on EU-regulated markets that exceed at least two of these thresholds :
- more than 10 employees
- more than 700 000 EUR in net turnover
- more than 350 000 EUR in total assets
CSRD will not cover enterprises with less than 10 employees or below 2 million EUR.
SMEs and other small and non-complex institutions must implement the CSRD and align to the ESRS from the financial year 2026. However, they will have the option to opt out of the reporting rules until 1st January 2028.
The fourth phase: 1st January 2028
Companies affected:
From the 1st of January 2028, CSRD will be applied to non-EU-country companies that meet the following requirements:
- a net turnover exceeding 150 million EUR in the EU and
- at least one subsidiary or branch in the EU.
How Worldfavor can help
Complying with the CSRD means handling a big chunk of data. Set up a smooth process for your data collection with Worldfavor that helps you collect, track and report your ESG data to get CSRD ready! Want to know more? Book a demo now!
Related blog posts you might like:






%20as%20the%20deadline%20approaches.%20Learn%20about%20compliance%20requirements%2c%20potential%20delays%2c%20and%20key%20updates..png)
